
Eggshells have been identified as a potential eco-friendly material for extracting rare earth elements necessary for green energy technologies.
A cracking discovery with the potential to make a significant impact in the sustainable recovery of rare earth elements (REEs) was made by a collaborative team of researchers. REEs are in increasing demand for use in green energy technologies. The team found that humble eggshell waste could recover REEs from water, offering a new, environmentally friendly method for their extraction.
The researchers, from Trinity College Dublin’s School of Natural Sciences, and iCRAG, the Science Foundation Ireland research center in applied geosciences, published their ground-breaking findings on June 4 in the international journal ACS Omega.
Demand and Supply Challenges for Rare Earth Elements
REEs, which are essential for the technologies used in electric cars and wind turbines, for example, are in increasing demand but in relatively short supply. As a result, scientists must find new ways of extracting them from the environment – and in sustainable ways, with current methods often harmful.
Here, the researchers discovered that calcium carbonate (calcite) in eggshells can effectively absorb and separate these valuable REEs from water.
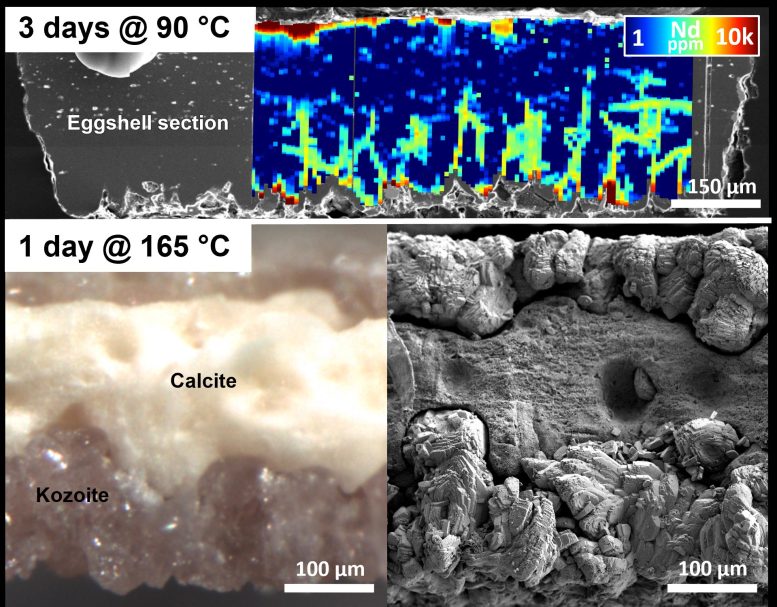
Experimental Methods and Temperature Effects on REE Recovery
The researchers placed eggshells in solutions containing REEs at various temperatures from a pleasant 25 °C (77 °F) to a scorching 205 °C (401 °F), and for different time periods of up to three months. They found that the elements could enter the eggshells via diffusion along the calcite boundaries and the organic matrix, and, at higher temperatures, that the rare earth built new minerals on the eggshell surface.
At 90 °C, the eggshell surface helped recover formations of a rare earth compound called kozoite. As things got hotter, the eggshells underwent a complete transformation with the calcite shells dissolving and being replaced by polycrystalline kozoite. And at the highest temperature of 205 °C (401 °F), this mineral gradually transitioned into bastnasite, the stable rare earth carbonate mineral that is used by industry to extract REEs for technology applications.
Impact and Implications of the Research
This innovative method suggests that waste eggshells could be repurposed as a low-cost, eco-friendly material to help meet the growing demand for REES, as the eggshells trap distinct rare earths within their structure over time.
Lead author Dr. Remi Rateau commented on the significance of the research, stating, “This study presents a potential innovative use of waste material that not only offers a sustainable solution to the problem of rare earth element recovery but also aligns with the principles of circular economy and waste valorization.”
Principal Investigator, Prof. Juan Diego Rodriguez-Blanco, emphasized the broader implications of the findings, adding: “By transforming eggshell waste into a valuable resource for rare earth recovery, we address critical environmental concerns associated with traditional extraction methods and contribute to the development of greener technologies.”
Work was conducted at the Department of Geology in the School of Natural Sciences, Trinity. iCRAG (Irish Centre for Research in Applied Geosciences) is an SFI centre dedicated to advancing geosciences research with a focus on sustainable resource management and environmental protection.
Reference: “Utilization of Eggshell Waste Calcite as a Sorbent for Rare Earth Element Recovery” by Rémi Rateau, Melanie Maddin, Adrienn M. Szucs, Luca Terribili, Kerstin Drost, Paul C. Guyett and Juan Diego Rodriguez-Blanco, 4 June 2024, ACS Omega.
DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00931
1 Comment
If Western Civilization wasn’t constantly trying to make enemies of every living thing on Earth, we could just buy everything we need from China.