Talin’s springy role in force transmission and dynamic cellular bridging.
Cell biology has possibly never jumped to the next level in the same way.
In multicellular organisms, cell migration and mechanosensing are essential for cellular development and maintenance. These processes rely on talin, the key focal adhesion — or FA — protein, central in connecting adjacent cellular matrices and enabling force transmission between them.
Talins are commonly considered fully extended at FAs between actin filaments — or F-actin — and the anchor-like integrin receptor.
Contradicting Prevailing Notions
However, a research team led by Kyoto University previously observed that the actin network constantly moves over FAs as a single unit: a unique phenomenon contradicting prevailing notions.
“This begs the question: how does talin manage to simultaneously maintain the intercellular connection while transmitting force?” asks corresponding author Sawako Yamashiro at KyotoU’s Graduate School of Life Sciences.
Most significantly, the team’s results reveal a new mode of force transmission in which dynamic molecular stretching bridges the extracellular matrix and flowing F-actin moving at different speeds. This discovery underscores the necessity of molecular elasticity and random coupling for sufficiently transmitting force.
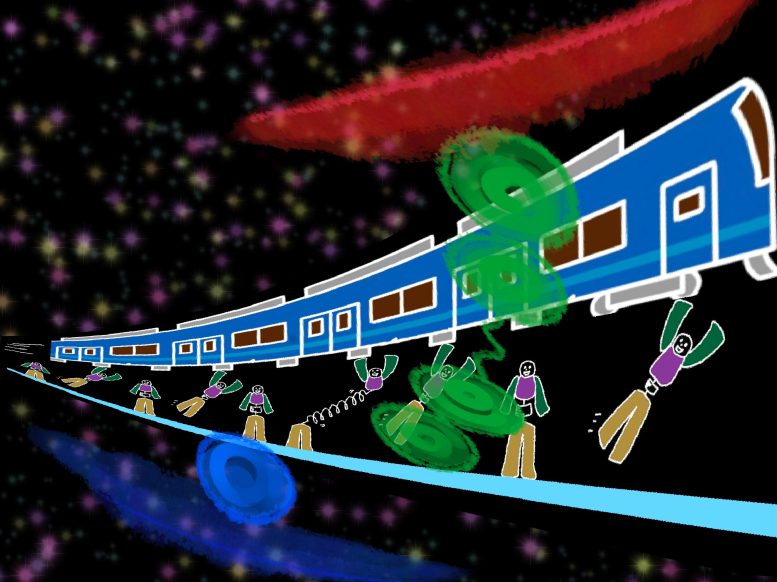

A New Model of Force Transmission
“On a human scale, this phenomenon can be visualized as a super flexible anime character. He is gripping onto a train passing at around 50 km/h,” illustrates Yamashiro.
The train represents the flowing F-actin, while a station platform is the substrate. The superhero plays the talin FA protein that would either be carried away unstretched or remain on the substrate.
“Occasionally, however, when both ends of talin are firmly anchored, it gets stretched by the pull because some parts of this protein can unfold like a spring,” explains Yamashiro.
Aided by intracellular fluorescent talin single-molecule imaging, Yamashiro’s team observed and calculated that approximately 4% of the talin links the F-actin and the substrate via an elastic transient clutch. In contrast, the remaining majority are bound to either end.
Revising Molecular Roles
These findings also call for revising the role of molecular unfolding, updating the traditional view that it functions as a mechanosensor and a shock absorber when molecules unfold under external force.
“However, our results suggest that molecular unfolding facilitates the transmission of force rather than absorbing it,” says coauthor Dimitrios Vavylonis at Lehigh University.
“We can expect further use of intracellular single-molecule microscopy to witness other possible intra- and extra-cellular superheroic behaviors, such as talin’s elastic transient clutch,” concludes coauthor Naoki Watanabe, also at KyotoU’s Graduate School of Life Sciences.
Reference: “Force transmission by retrograde actin flow-induced dynamic molecular stretching of Talin” by Sawako Yamashiro, David M. Rutkowski, Kelli Ann Lynch, Ying Liu, Dimitrios Vavylonis and Naoki Watanabe, 20 December 2023, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44018-z