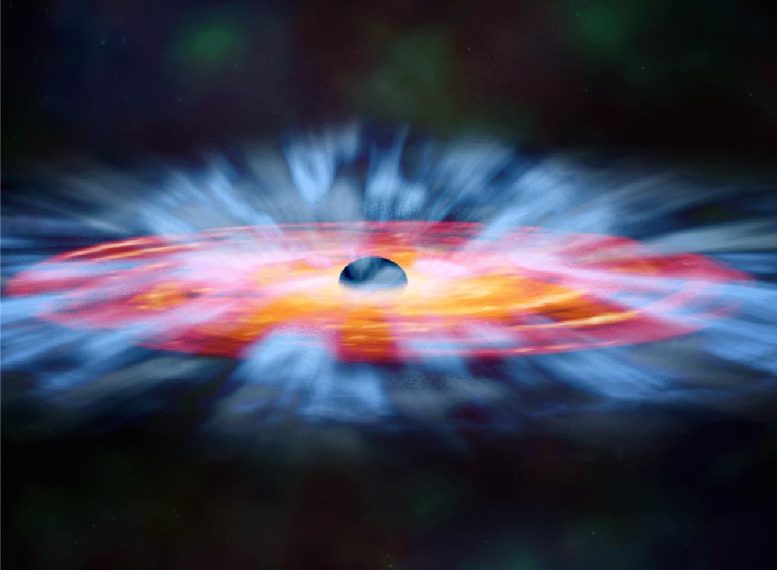

A new discovery helps illuminate how active black holes can continuously shape their galaxies by spurring on or snuffing out the development of new stars.
Astronomical research reveals that supermassive black holes accelerate gas in galaxies, significantly affecting star development through powerful winds. This study adds crucial insights into how black holes shape their galaxies.
Cosmic Dynamics: Gas Acceleration in Galaxies
Clouds of gas in a distant galaxy are being pushed faster and faster — at more than 10,000 miles per second — out among neighboring stars by blasts of radiation from the supermassive black hole at the galaxy’s center. It’s a discovery that helps illuminate the way active black holes can continuously shape their galaxies by spurring on or snuffing out the development of new stars.
A team of researchers led by University of Wisconsin–Madison astronomy professor Catherine Grier and recent graduate Robert Wheatley revealed the accelerating gas using years of data collected from a quasar, a particularly bright and turbulent kind of black hole, billions of light-years away in the constellation Boötes. They presented their findings at the 244th meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Madison.
Scientists believe black holes are situated at the center of most galaxies. Quasars are supermassive black holes surrounded by disks of matter being pulled in by the black hole’s enormous gravitational power.
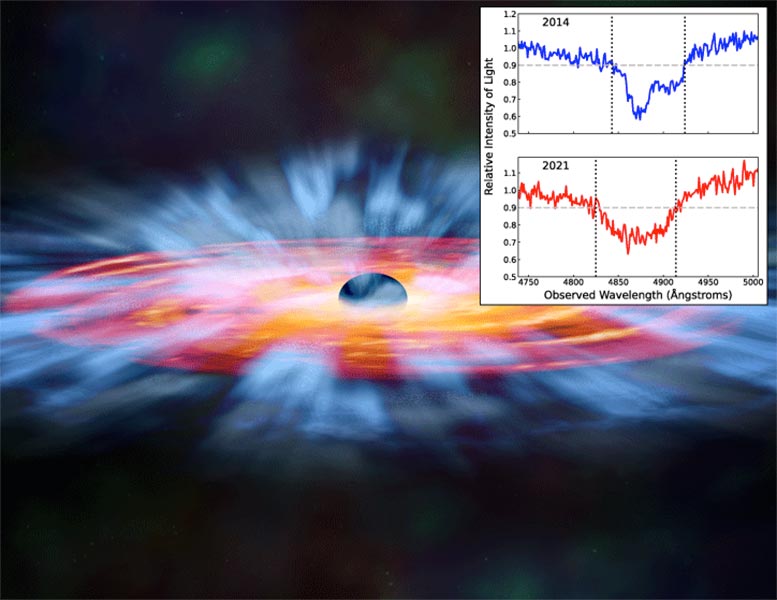
The Mechanisms of Quasar Illumination
“The material in that disk is always falling into the black hole, and the friction of that pulling and pulling heats up the disk and makes it very, very hot and very, very bright,” says Grier. “These quasars are really luminous, and because there’s a large range of temperatures from the interior to the far parts of the disk, their emission covers almost all of the electromagnetic spectrum.”
The bright light makes quasars nearly as old as the universe (as many as 13 billion light years away) visible, and the broad range of their radiation makes them particularly useful for astronomers to probe the early universe.

Observational Insights into Black Hole Winds
Researchers used more than eight years of observations of a quasar called SBS 1408+544, collected by a program carried out by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey now known as the Black Hole Mapper Reverberation Mapping Project. They tracked winds composed of gaseous carbon by spotting light from the quasar that was missing — light that was being absorbed by the gas. But instead of being absorbed at exactly the right spot in the spectrum that would indicate carbon, the shadow shifted farther from home with every new look at SBS 1408+544.
“That shift tells us the gas is moving fast, and faster all the time,” says Wheatley. “The wind is accelerating because it’s being pushed by radiation that is blasted off of the accretion disk.”
Scientists, including Grier, have suggested they’ve observed accelerating winds from black hole accretion disks before, but this had not yet been backed by data from more than a few observations. The new results came from about 130 observations of SBS 1408+544 made over nearly a decade, which allowed the team to solidly identify the increase in velocity with high confidence.
The Influence of Black Hole Winds on Galactic Evolution
The winds pushing gas out from the quasar are of interest to astronomers because they are a way in which the supermassive black holes might influence the evolution of the galaxies that surround them.
“If they’re energetic enough, the winds may travel all the way out into the host galaxy, where they could have a significant impact,” Wheatley says.
Depending on the circumstances, a quasar’s winds could supply pressure that squeezes gas together and speeds the birth of a star in its host galaxy. Or it could scour away that fuel and keep a potential star from forming.
“Supermassive black holes are big, but they’re really tiny compared to their galaxies,” says Grier, whose work is supported by the National Science Foundation. “That doesn’t mean they can’t ‘talk’ to each other, and this is a way for one to talk to the other that we will have to account for when we model the effects of these kinds of black holes.”
The study of SBS 1408+544 was published on June 11 in The Astrophysical Journal.
Reference: “The SDSS-V Black Hole Mapper Reverberation Mapping Project: C iv Broad Absorption Line Acceleration in the Quasar SBS 1408+544” by Robert Wheatley, Catherine J. Grier, Patrick B. Hall, W. N. Brandt, Jonah Lotz, D. P. Schneider, Jonathan R. Trump, Yue Shen, Lucas M. Seaton, Scott F. Anderson, Matthew J. Temple, Roberto Assef, Logan B. Fries, Y. Homayouni, Darshan Kakkad, Anton M. Koekemoer, Mary Loli Martínez-Aldama, C. Alenka Negrete, Claudio Ricci, Dmitry Bizyaev, Joel R. Brownstein, Sean Morrison and Kaike Pan, 11 June 2024, The Astrophysical Journal.
DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad429e
The study included collaborators at York University, Pennsylvania State University, University of Arizona, and others.
This research was funded in part by grants from the National Science Foundation (AST-2310211 and AST-2309930).