- By analyzing duplicates of thousands of genes, researchers have reconstructed the evolutionary events leading to the creation of eukaryotic cells, the precursors to virtually all life you can see with the naked eye.
- The evolutionary timeline from simple bacterial cells to complex eukaryotic cells progressed differently than previously thought.
- The study, a collaboration between the Comparative Genomics lab at IRB Barcelona and the University of Utrecht, has been published in Nature Ecology & Evolution.
One of the most important and puzzling events in the evolution of life has been the origin of the first complex eukaryotic cells. Almost all lifeforms that we can perceive with the naked eye, such as algae, plants, animals, and fungi, are made up of complex cells known as ‘eukaryotes.’ A collaborative study between the groups of Toni Gabaldón, ICREA researcher at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and the Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC-CNS), and Berend Snel at the University of Utrecht, has concluded that the first cell to incorporate a mitochondrion (considered the key step to the increased complexity of eukaryotic cells) already presented eukaryote-like complexity in structure and functions. This scenario serves as a bridge between the signs of complexity observed in some archaeal genomes and the proposed role of mitochondria in triggering eukaryogenesis.
“The acquisition of mitochondria was considered either to be the crucial first step or the last step in the development of eukaryotic cell complexity,” explains Gabaldón, “our findings show that it was indeed a crucial event, but that it happened in a scenario where cell complexity had already increased.”
Complexity as a prelude to the diversity of life
For roughly the first half of the history of life on Earth, the only forms of life were the relatively simple cells of bacteria. “Eukaryotic cells are larger, contain more DNA, and are made up of compartments, each with their own task,” explains first author Julian Vosseberg. “In that sense, you could compare bacterial cells with a tent, while eukaryotic cells are more like houses with several rooms.”
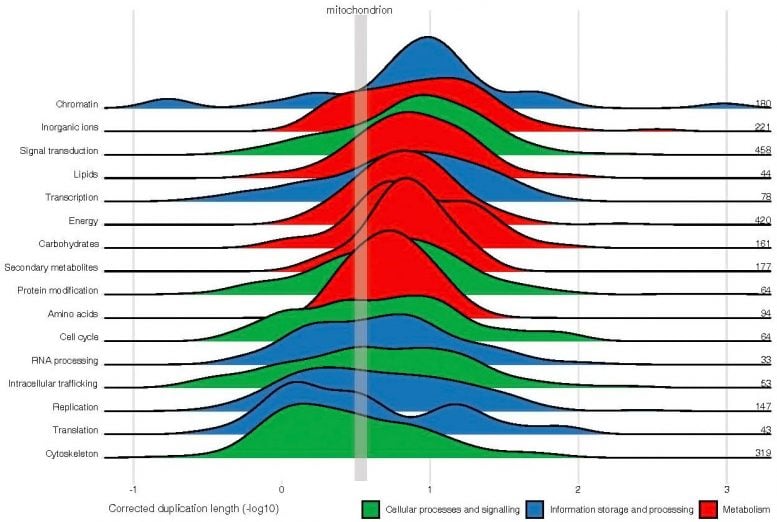
How and when organisms traded the tent for a house is still a mystery, as there are no intermediate forms. One important moment in evolution was the origin of mitochondria, a component of eukaryotic cells that function as their ‘power plants’. Mitochondria were once free-living bacteria, but during evolution, they were absorbed by the ancestors of today’s eukaryotic cells. As gene duplication probably drove the increase in cell complexity, the researchers attempted to reconstruct the evolutionary events based on these genetic changes.
Bioinformatics for evolutionary path reconstruction
“We can use the DNA of contemporary species to reconstruct evolutionary events. Our genes were formed over aeons of evolution. They have changed dramatically over that time, but they still hold echoes of a distant past.” Vosseberg adds, “We have a vast quantity of genetic material available, from a variety of organisms, and we can use computers to reconstruct the evolution of thousands of genes, including ancient gene duplications. These reconstructions have enabled us to uncover the timing of important intermediate steps.”
The co-corresponding author, Berend Snel, from the University of Utrecht, says, “Scientists did not have a timeline of these events. But now we’ve managed to reconstruct a rough timeline.” To achieve this, the researchers adapted an existing method developed at Gabaldon’s lab to create a new protocol, which has resulted in novel insights. These indicate that a lot of complex cellular machinery had evolved even before the symbiosis with mitochondria, including the development of transport within the cell and the cytoskeleton. “The symbiosis wasn’t an event that served as the catalyst for everything else. We observed a peak in gene duplications much earlier in time, indicating that cell complexity had already increased before that moment,” says Snel.
“Our study suggests that the ancestral host that acquired the mitochondrial endosymbiont had already developed some complexity in terms of a dynamic cytoskeleton and membrane trafficking,” says Gabaldón “this might have favored the establishment of symbiotic associations with other microorganisms, including the mitochondrial ancestor, which eventually became integrated.”
Reference: “Timing the origin of eukaryotic cellular complexity with ancient duplications” by Julian Vosseberg, Jolien J. E. van Hooff, Marina Marcet-Houben, Anne van Vlimmeren, Leny M. van Wijk, Toni Gabaldón and Berend Snel, 26 October 2020, Nature Ecology & Evolution.
DOI: 10.1038/s41559-020-01320-z