
Diversity is key to resilience, says new study.
If you were planning to drink your way through the climate apocalypse, here’s some unfortunate news: Just as climate change threatens homes, food, and livelihoods, so does it threaten the world’s supply of wine. If temperatures rise by 2 degrees Celsius (3.6 degrees Fahrenheit), the regions of the world that are suitable for growing wine grapes could shrink by as much as 56 percent, according to a new study. And with 4 degrees Celsius (7.2 degrees Fahrenheit) of warming, 85 percent of those lands would no longer be able to produce good wines.
Fortunately for wine-lovers, however, the new study also outlines an adaptation strategy. The findings indicate that reshuffling where certain grape varieties are grown could halve the potential losses of winegrowing regions under 2 degrees of warming, and reduce losses by a third if warming reaches 4 degrees. The study is published today (January 27, 2020) in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.

Scientists have long suspected that crop diversity is key to making agriculture more resilient to climate change, and wine grapes offer a unique opportunity to test this assumption. They are both extremely diverse — there are more than 1,100 different varieties planted today, growing under a wide range of conditions — and well-documented, with harvest data stretching back centuries. Wine grapes are also extremely sensitive to the changes in temperature and season that come with climate change.
“In some ways, wine is like the canary in the coal mine for climate change impacts on agriculture, because these grapes are so climate-sensitive,” said co-author Benjamin Cook from Columbia University’s Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory and the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies.
Cook and colleagues investigated whether utilizing this wide diversity of wine grapes could help to build resiliency. Their findings may help other areas of agriculture adapt to a warming world.
The researchers — led by Ignacio Morales-Castilla at the University of Alcalá in Spain and Elizabeth Wolkovich at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver — focused on 11 varieties of wine grape, based on their diversity in development timing, a key trait for climate adaptation. The researchers selected cabernet sauvignon, chasselas, chardonnay, grenache, merlot, monastrell (also known as mourvedre), pinot noir, riesling, sauvignon blanc, syrah and ugni blanc.
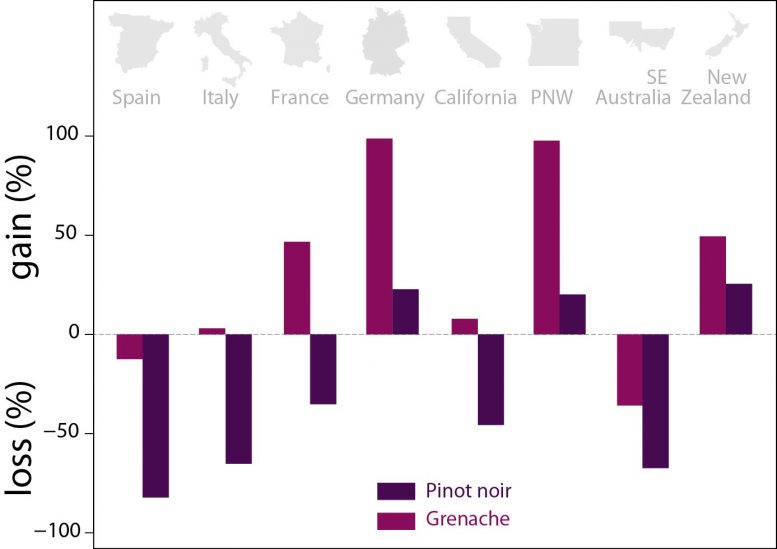
For the 11 varieties, the team used vinter and researcher archives to build a model for when each would bud, flower, and ripen in winegrowing regions around the world under three different warming scenarios: 0, 2, and 4 degrees of warming. Then they used climate change projections to see where those varieties would be viable in the future.
Losses were unavoidable in both warming scenarios, due to shifting temperatures and seasonal changes that would affect conditions while the varieties were ripening. These factors would affect the wines’ quality. But the team found that “by switching these varieties around, you can reduce losses by a significant amount,” said Cook.
With 2 degrees of global warming and no attempts at adaptation, 56 percent of the world’s winegrowing areas may no longer be suitable for growing wine. But if wine growers switch to varieties more suitable for the changing climate, only 24 percent would be lost. For example, in France’s Burgundy region, heat-loving mourvedre and grenache could replace current varieties such as pinot noir. In Bordeaux, cabernet sauvignon and merlot could be replaced with mourvedre.
The scientists say that cooler winegrowing regions such as Germany, New Zealand, and the U.S. Pacific Northwest would be relatively unscathed in the 2°C scenario. These areas could become suitable for warmer varieties like merlot and grenache, while varieties that prefer cooler temperatures, such as pinot noir, could expand northward into regions that are not currently suitable for growing wine.
Winegrowing regions that are already hot now — such as Italy, Spain, and Australia — faced the largest losses, because they are already limited to planting the warmest varieties.
The variety-swapping was less effective at higher amounts of global warming. With 4 degrees of warming, planting climate-specific varieties reduced losses from 85 to 58 percent, or approximately a third.
Switching wine grape varieties could come with significant — but not insurmountable — legal, cultural, and financial challenges. “Conversations in Europe have already begun about new legislation to make it easier for major regions to change the varieties they grow,” said Wolkovich. “But growers still must learn to grow these new varieties. That’s a big hurdle in some regions that have grown the same varieties for hundreds and hundreds of years, and they need consumers who are willing to accept different varieties from their favorite regions.”
The researchers note that management practices like increased irrigation and using shade cloths can also help to protect grapevines, but only at lower levels of warming.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of any strategy depends on growers having the options and resources to adapt at a local scale, and on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and limiting warming globally, the authors say.
“The key is that there are still opportunities to adapt viticulture to a warmer world,” said Cook. “It just requires taking the problem of climate change seriously.”
Reference: “Diversity buffers winegrowing regions from climate change losses” by Ignacio Morales-Castilla, Iñaki García de Cortázar-Atauri, Benjamin I. Cook, Thierry Lacombe, Amber Parker, Cornelis van Leeuwen, Kimberly A. Nicholas and Elizabeth M. Wolkovich, 27 January 2020, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1906731117
Other authors on the paper include: Iñaki García de Cortázar-Atauri and Thierry Lacombe of the Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique; Amber Parker of Lincoln University, New Zealand; Cornelis van Leeuwen of Bordeaux Sciences Agro; and Kimberly A. Nicholas of Lund University.
Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory is Columbia University’s home for Earth science research. Its scientists develop fundamental knowledge about the origin, evolution and future of the natural world, from the planet’s deepest interior to the outer reaches of its atmosphere, on every continent and in every ocean, providing a rational basis for the difficult choices facing humanity.
The Earth Institute, Columbia University mobilizes the sciences, education and public policy to achieve a sustainable earth.