New study uses 3D printing and genetically modified plant cells to create complex, self-repairing materials that could revolutionize biomanufacturing and construction.
Scientists are harnessing cells to make new types of materials that can grow, repair themselves and even respond to their environment. These solid “engineered living materials” are made by embedding cells in an inanimate matrix that’s formed in a desired shape.
Now, researchers report today (May 1) in ACS Central Science that they have 3D printed a bioink containing plant cells that were then genetically modified, producing programmable materials. Applications could someday include biomanufacturing and sustainable construction.
Exploring Plant Cells in Material Engineering
Recently, researchers have been developing engineered living materials, primarily relying on bacterial and fungal cells as the live component. However, the unique features of plant cells have stirred enthusiasm for their use in engineered plant living materials (EPLMs).
Previously, the plant cell-based materials created by scientists have had fairly simple structures and limited functionality. Ziyi Yu, Zhengao Di, and colleagues wanted to change that by making intricately shaped EPLMs containing genetically engineered plant cells with customizable behaviors and capabilities.

Innovative 3D Printing Techniques
The researchers mixed tobacco plant cells with gelatin and hydrogel microparticles that contained Agrobacterium tumefaciens, a bacterium commonly used to transfer DNA segments into plant genomes.
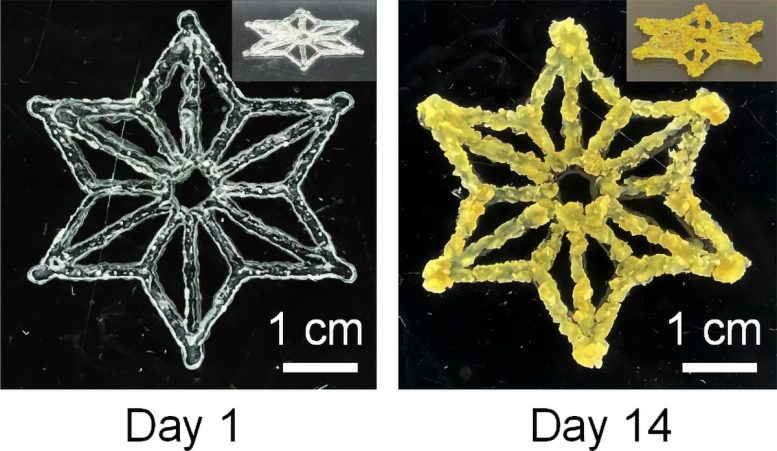
This bioink mixture was then 3D printed on a flat plate or inside a container filled with another gel to form shapes such as grids, snowflakes, leaves, and spirals. Next, the hydrogel in the printed materials was cured with blue light, hardening the structures. During the ensuing 48 hours, the bacteria in the EPLMs transferred DNA to the growing tobacco cells.
The materials were then washed with antibiotics to kill the bacteria. In the following weeks, as the plant cells grew and replicated in the EPLMs, they began producing proteins dictated by the transferred DNA.
Proof-of-Concept and Future Applications
In this proof-of-concept study, the transferred DNA enabled the tobacco plant cells to produce green fluorescent proteins or betalains — red or yellow plant pigments that are valued as natural colorants and dietary supplements. By printing a leaf-shaped EPLM with two different bioinks — one that created red pigment along the veins and the other a yellow pigment in the rest of the leaf — the researchers showed that their technique could produce complex, spatially controlled, and multifunctional structures.
Such EPLMs, which combine the traits of living organisms with the stability and durability of non-living substances, could find use as cellular factories to churn out plant metabolites or pharmaceutical proteins, or even in sustainable construction applications, according to the researchers.
Reference: “Advancing Engineered Plant Living Materials through Tobacco BY-2 Cell Growth and Transfection within Tailored Granular Hydrogel Scaffolds” by Yujie Wang, Zhengao Di, Minglang Qin, Shenming Qu, Wenbo Zhong, Lingfeng Yuan, Jing Zhang, Julian M. Hibberd and Ziyi Yu, 1 May 2024, ACS Central Science.
DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.4c00338
The authors acknowledge funding from National Key Research and Development Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, and the State Key Laboratory of Materials-Oriented Chemical Engineering.