When and why does a photon emitter fail to emit? Research at UC Santa Barbara sheds light on this question.
Research on quantum internet technology highlights the challenge of producing stable photons at telecom wavelengths, with recent studies focusing on material improvements and advanced emission techniques to enhance quantum network efficiency.
Computers benefit greatly from being connected to the internet, so we might ask: What good is a quantum computer without a quantum internet?
The secret to our modern internet is the ability for data to remain intact while traveling over long distances, and the best way to achieve that is by using photons. Photons are single units (“quanta”) of light. Unlike other quantum particles, photons interact very weakly with their environment. That stability also makes them extremely appealing for carrying quantum information over long distances, a process that requires maintaining a delicate state of entanglement for an extended period of time. Such photons can be generated in a variety of ways. One possible method involves using atomic-scale imperfections (quantum defects) in crystals to generate single photons in a well-defined quantum state.
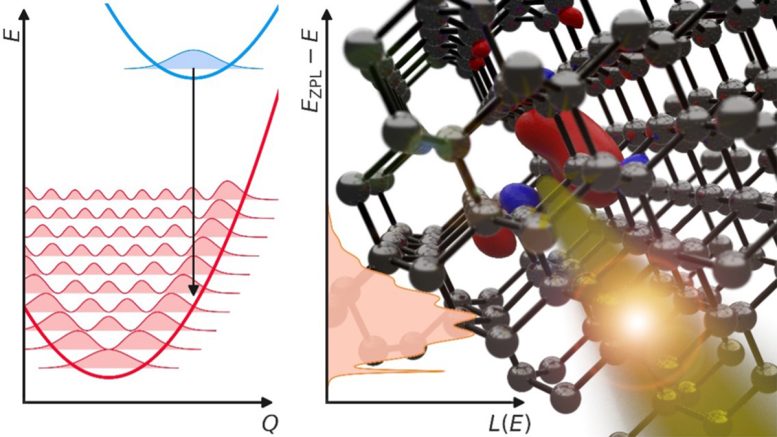
Decades of optimization have resulted in fiber-optic cables that can transmit photons with extremely low loss. However, this low-loss transmission works only for light in a narrow range of wavelengths, known as the “telecom wavelength band.” Identifying quantum defects that produce photons at these wavelengths has proven difficult, but funding from the U.S. Department of Energy and the National Science Foundation (NSF) has enabled researchers in the UC Santa Barbara College of Engineering to understand why that is. They describe their findings in a paper recently published in the journal APL Photonics.
Quantum Emission Efficiency
“Atoms are constantly vibrating, and those vibrations can drain energy from a light emitter,” says UCSB materials professor Chris Van de Walle. “As a result, rather than emitting a photon, a defect might instead cause the atoms to vibrate, reducing the light-emission efficiency.” Van de Walle’s group developed theoretical models to capture the role of atomic vibrations in the photon-emission process and studied the role of various defect properties in determining the degree of efficiency.
Their work explains why the efficiency of single-photon emission drastically decreases when the emission wavelength increases beyond the wavelengths of visible light (violet to red) to the infrared wavelengths in the telecom band. The model also allows the researchers to identify techniques for engineering emitters that are brighter and more efficient.
“Choosing the host material carefully, and conducting atomic-level engineering of the vibrational properties are two promising ways to overcome low efficiency,” said Mark Turiansky, a postdoctoral researcher in the
Van de Walle lab, a fellow at the NSF UC Santa Barbara Quantum Foundry, and the lead researcher on the project.
Another solution involves coupling to a photonic cavity, an approach that benefited from the expertise of two other Quantum Foundry affiliates: computer engineering professor Galan Moody and Kamyar Parto, a graduate student in the Moody lab.
The team hopes that their model and the insights it provides will prove useful in designing novel quantum emitters that will power the quantum networks of the future.
Reference: “Rational design of efficient defect-based quantum emitters” by Mark E. Turiansky, Kamyar Parto, Galan Moody and Chris G. Van de Walle, 26 June 2024, APL Photonics.
DOI: 10.1063/5.0203366
1 Comment
The team hopes that their model and the insights it provides will prove useful in designing novel quantum emitters that will power the quantum networks of the future.
Ask researchers to think deeply:
1. What is the physical reality described by quantum theory?
2. Can quantum theory describe the superposition and entanglement of topological vortices?
3. Is the superposition, deflection, and entanglement of topological vortices a physical reality?
and so on.
Spin is crucial in the evolution of spacetime motion of cosmic matter.
Based on the ideal fluid physics characteristics of space, there is no eternal mass, but eternal fluid mechanics. In the interaction and balance of topological vortex fractal structures, spin creates everything (including gravity), and spin creates the world.
The universe does not make algebra, formulas, or fractions. The universe is a superposition, deflection, and entanglement of geometric shapes, is the interaction and balance of countless topological vortex fractal structures. In these interaction and balance, the past is difficult to change. For the future, some predictable, some unpredictable. But, the present moment is real, certain, and actionable. Physics should not ignore that low dimensional topological fractal structures are the material basis of high-dimensional spacetime.
Scientific research guided by correct theories can help humanity avoid detours, failures, and pomposity. Please witness the exemplary collaboration between theoretical physicists and experimentalists (https://scitechdaily.com/microscope-spacecrafts-most-precise-test-of-key-component-of-the-theory-of-general-relativity/#comment-854286). Some people in contemporary physics has always lived in a self righteous children’s story world. Whose values have been overturned by such a comical and ridiculous reality?
Misguided by the pseudo-scientific theory of Physical Review Letters (PRL), many researchers do not consider the similarities and differences between geometric shapes and physical reality in physics research, but indulge in imagination, and some scholars’ physics research seriously deviates from science, and they are almost unaware of the dirtiness and ugliness. Although mathematics is the language of science, it must be understood correctly.